Dashboards are magical.
They are cute little Pandora boxes that provide you with the best of business insights at the ease of your finger tips.
Human affinity for data and trying to make sense of it is undeniable.
Be it the Egyptians circa 300 BC trying to capture all ‘data’ available in the library of Alexandria or Ptolemy circa 200 AD making a database of Greek constellations in his Almagest, one pattern is prevalent.
The data humans interact with tends to be in visual forms.
The difference is staggeringly simple: We have eyes to process large amounts of visual imagery but we do not have analytical engines in our brains to process large amounts of numeric data. And amusingly enough, this is exactly why there is an entire field of computing known as computer vision only to imitate the way human eyes process data.
The world is still adapting to the data revolution. We are still trying to make sense of the profundity of data available to us. The following graph puts the exponentiality of human data production into perspective:
Total data volume worldwide 2010-2024
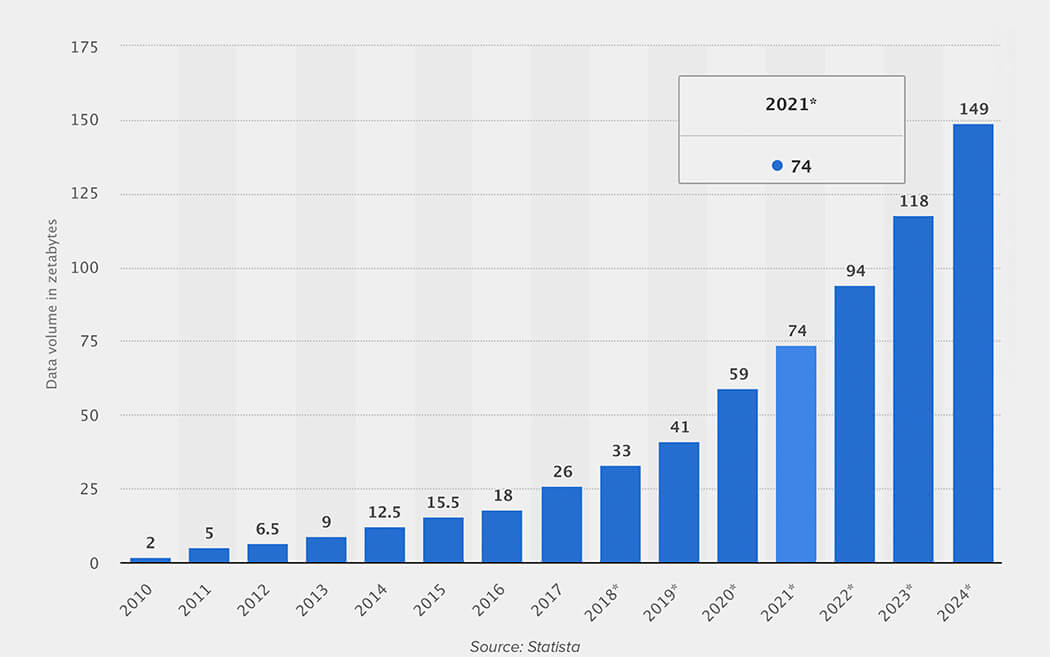
So the real question is: What do we do with all this data?
The answer is simple: We analyze it.
But how do we analyze it? Visually.
The true utility of big data is that it helps make BETTER decisions!
It does not matter whether you are a C-class employee of a Fortune 500 firm or a middle school teacher running your day-to-day errands. Data based predictions ultimately find their way into your life. From Google Maps predicting the best traffic route to Power BI predicting your quarterly sales volume, data-oriented decisions are increasingly becoming an inseparable part of our lives.

In such a setting, it becomes paramount for businesses and organizations to keep up with data technologies to make the most informed decisions.
This “keeping up” fundamentally drills down to making data more and more human readable. This is where dashboards come in. They visualize data for us.
Data-visualization technologies are constantly evolving, with data scientists continuously experimenting. Today’s dashboard scene is not as it used to be twenty years ago, nor is it the way it will be twenty years in the future.
Following are today’s most popular methods of visualizing data listed along-with their pros:
1. Area Chart
- Helpful for showing Key Performance Indicators.
- Extremely helpful in spotting, analyzing, and comparing data trends.
2. Streamgraph
- Can display and compare different data entities high-volume datasets.
- Packs high-density information.
3. Scatter Plot (2D or 3D)
- Well-suited to display non-linear patterns.
- Incorporates range of data flow i.e. maxima and minima.
4. Column & Bar Chart
- Can be used with both numerical and categorical data.
- Widely used hence user familiarity.
- Shows each data category in a frequency distribution.
5. Circle View/Pie & Donut Chart
- Displays relative proportions of different categories of data.
- Easy to consume for users.
Need to build an enterprise grade product?
We replace old enterprise implementations with the latest technology, custom built for better scale, security, usability and value.
6. Wedge Stack/Radar Graph
- Enables visualization of hierarchical data in radial systems.
- Can illustrate multilevel frequency data.
7. Gantt Chart
- Exhibits project progress and deadlines.
- Helps with resource load management.
- Improves project time management.
8. Timeline Chart
- Specializes in displaying time-bound activities.
- Can be incorporated into gantt charts.
9. Box-and-whisker Plot Chart
- Visualizes a variable’s location and spread.
- Shows outliers.
- Indicates data’s symmetry and skewness.
10. Cartogram Chart
- Projects data onto maps.
- Shows outliers.
- Visualizes relationships between data and geography.
11. Dot Distribution Map
- Displays density differences on geographical bases.
- Shows cluster-formation of data.
12. Tree Map
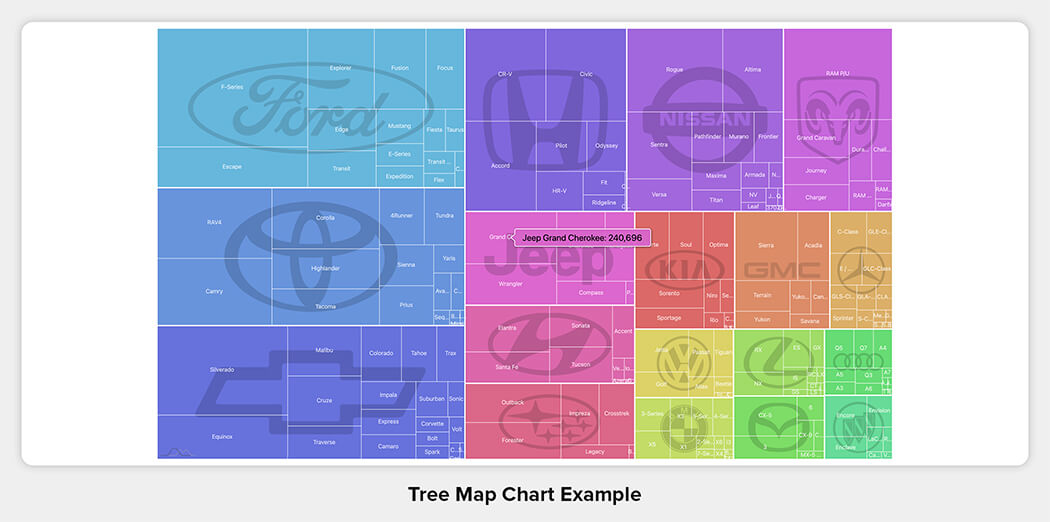
- Visualizes hierarchical relationships.
- Groups relevant elements together.
13. Radial Tree
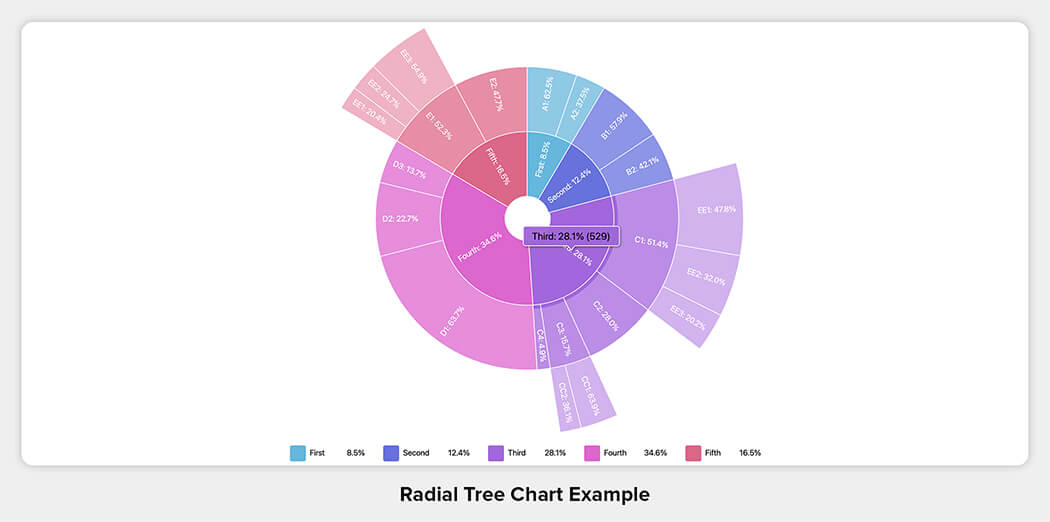
- Eases human consumption of tree data.
- Aptly visualizes chronological and probabilistic comparisons.
14. Heat Map
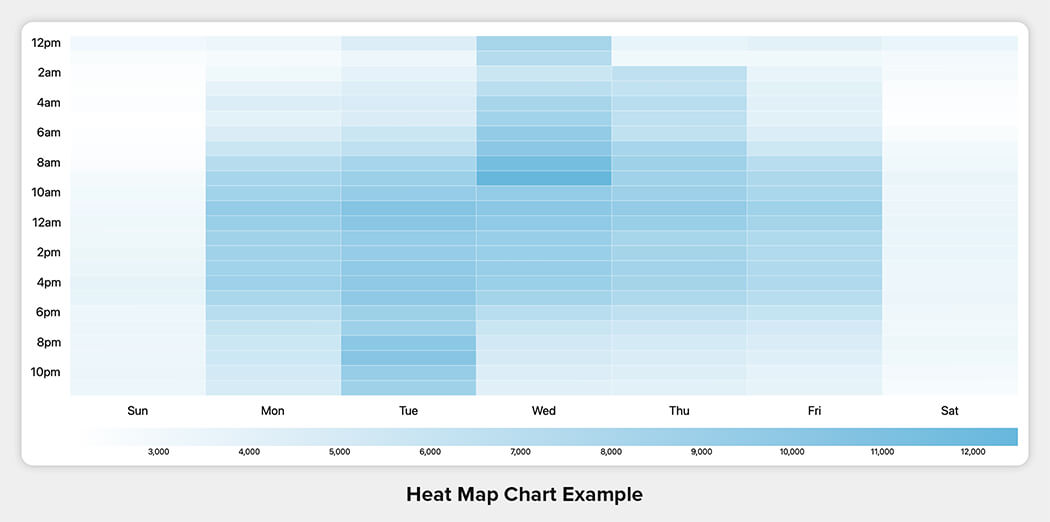
- Presents complex data-point volumes into human readable forms.
- Distributes color-coded frequencies over real-time entities.
- Extremely helpful in digital marketing.
15. Word Cloud

- Captures essence of high-volume textual data online.
- Helps pick social, political, and emotional trends worldwide.
16. Highlight Table
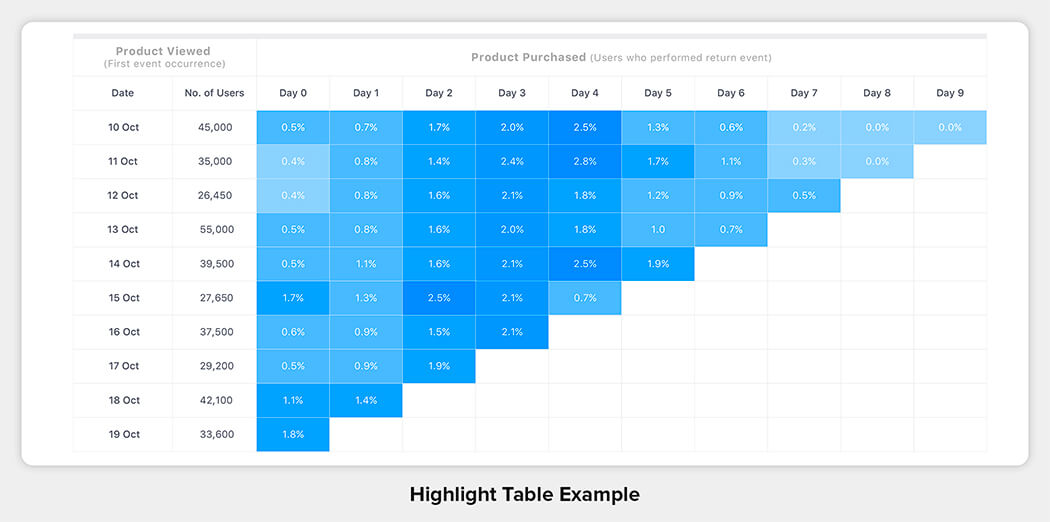
- Compares categorical data in textual form.
- Provides qualitative comparisons.
- Can be color-coded.
17. Histogram
- Displays frequencies with respect to intervals.
- Visualizes grouped data.
18. Bubble Cloud/Chart
- Can visualize three-dimensional data.
- Can incorporate a fourth variable as well (by assigning colors to bubbles).
19. Bullet Graph
- Can be oriented both, horizontally and vertically.
- Can display multiple measures simultaneously.
Need to build a web application?
With cross platform compatibility, web apps remain the ultimate medium for a product. Tell us about your project for a free consult.
20. Matrix Chart
- Can display both, qualitative and quantitative data.
- Enables visual juxtaposition of different genders of data.
21. Network Chart
22. Polar Area/Coxcomb/Rose Chart
- Enables radial comparison of magnitudes of quantitative data.
- Packs high-density information.
But these are only twenty-two? What’s the twenty-third?
The twenty-third and the most important of all is that the world doesn’t end here! You may equally design any mishmash of the above visualization methods for your dashboard, customfit to your own needs.
Sky’s the limit!
 Web Applications
Build web apps using cutting-edge technology
Web Applications
Build web apps using cutting-edge technology
 Business Intelligence Apps
Empower your business with fast & actionable BI Apps
Business Intelligence Apps
Empower your business with fast & actionable BI Apps
 Mobile Applications
Build cross-platform apps for iOS and Android devices
Mobile Applications
Build cross-platform apps for iOS and Android devices
 Internet of Things Apps
Streamline your operations with cloud-based IoT apps
Internet of Things Apps
Streamline your operations with cloud-based IoT apps
 AI Products
Unlock the power of AI & ML with our expertise
AI Products
Unlock the power of AI & ML with our expertise
 Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Mitigate risks & accelerate your project development
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Mitigate risks & accelerate your project development
 Enterprise Software
Build custom enterprise solutions for your business
Enterprise Software
Build custom enterprise solutions for your business
 Software as a Service (SaaS)
Scale your business with ease and cost-efficiency
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Scale your business with ease and cost-efficiency




























